You can view the following examples via this token: NjQzfGdsRDFqeXVV
Note: it is necessary to input the correct nominal power and nominal temperature delta on all the boiler types to have a baseline for relative flow and power in efficiency lookup. According to the actual boiler you are working with.
In Hysopt there are three boiler types:
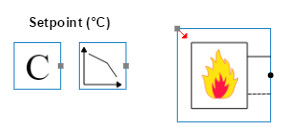
- Boiler with setpoint
The simplified boiler model generates the temperature that is given as a setpoint. The posted fuel consumption is the energy that is needed to reach the set point depending on the incoming return temperature and volume flow rate. The only parameter on this base circuit is a KV-value.
Image 1: Boiler with setpoint
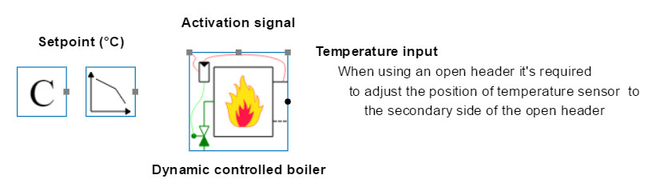
- Dynamic controlled boiler
The dynamic boiler model is a more detailed boiler model. This base circuit has its own control loop, which controls a gas valve in function of the measured supply temperature. In function of a three-dimensional matrix (volume flow rate, return temperature and modulation power) the model generates a fuel consumption and secondary heat flow. Therefore there are a lot more parameters as on the simplified boiler model. For example, you can adjust the boiler capacitance (water content and mass of steel), activation and deactivation threshold integral etc.
Image 2: Dynamic boiler model
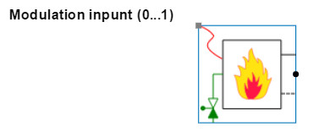
- Heat flow controlled boiler
The heat flow controlled boiler model is similar to the dynamic model with the only exception that this model has no internal control loop. The user must apply a control loop on the boiler model, the input on this model is a power modulation signal (0..1). This model is primarily used for making a cascade control between several boilers, an example can be find in the Hysopt inspiration library: NjMwfFFyQzJwNUlI
Image 3: Heat flow controlled boiler model