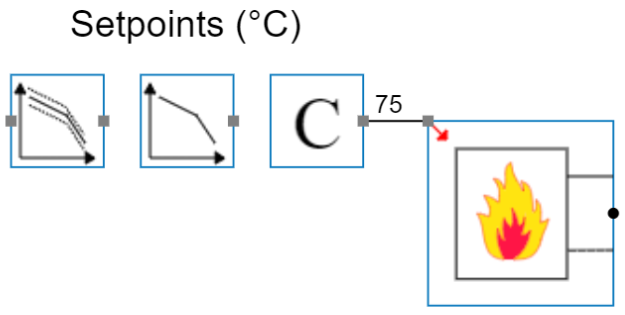
Boilers
In Hysopt there are 4 boiler types:
Boiler with setpoint
The simplified boiler model generates the temperature that is given as a setpoint. The setpoint can vary depending on the chosen control Base Circuit (BC), and it is connected to the upper left corner of the boiler BC. More information on the setpoints can be found in Generator.
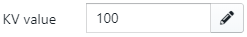
The only parameter needed for the design of the system is the KV value. The KV value is needed to calculate the pump head.
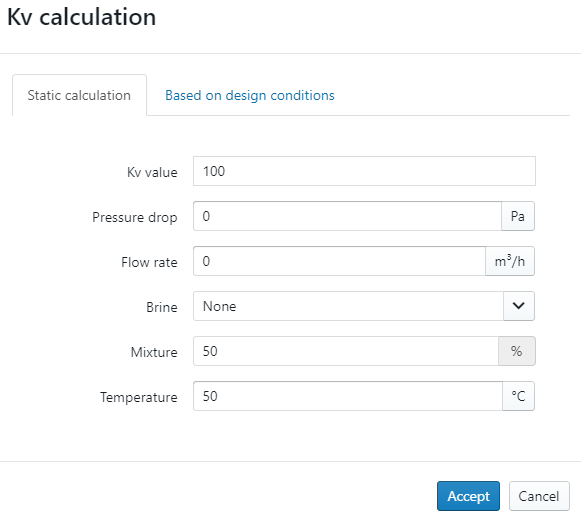
If the actual KV value isn't known, the user can click on the "pencil" icon which results in a calculation popup window. In the popup window, the user can calculate the KV value by entering the pressure drop and flow rate (and if needed, the brine, mixture and reference temperature). This option is preferred when the information on the boiler is known. However, the user can also let the software automatically calculate the KV value depending on the design flow rate by using the other tab and entering the estimated pressure drop over the boiler.
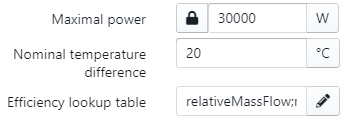
For an accurate simulation and representation of the system, the following parameters are needed:
The maximal power is automatically filled in after doing the "Compute design flows". If the user has an actual boiler which has a different thermal power than the system behind it, the user can enter it and lock it by clicking on the "lock" icon. The nominal temperature difference is needed to set scale the efficiency lookup table and is default 20°C. The efficiency lookup table is used during simulation to accurately simulate the primary power and efficiency of the boiler both in full and partial load.
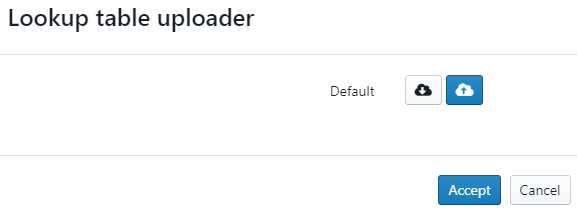
The user can insert and change the efficiency lookup table by clicking on the "pencil" icon. With the popup window, the user can download the CSV file by clicking on the "gray cloud" icon and change it. After changing it in Excel, the user can upload the corrected lookup table by clicking on the "blue cloud" icon and accepting it.
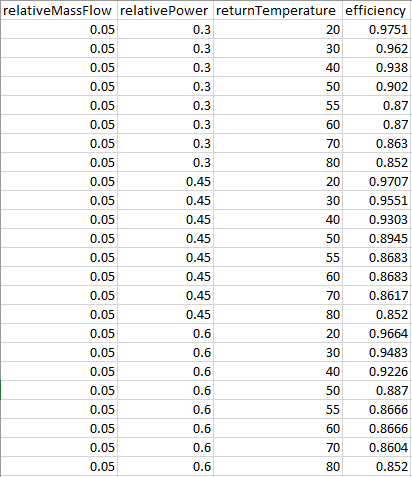
The data needed to update the efficiency table is "relative mass flow", "relative power", "return temperature" and "efficiency". Depending on the three-dimensional matrix (relative mass flow, relative power, and return temperature) the efficiency of the boiler can vary. If the manufacturer-specific information is known, the user can enter this into the efficiency table to accurately simulate the boiler. If the user doesn't have the necessary information, the default efficiency table is sufficiently accurate to represent a common boiler model.
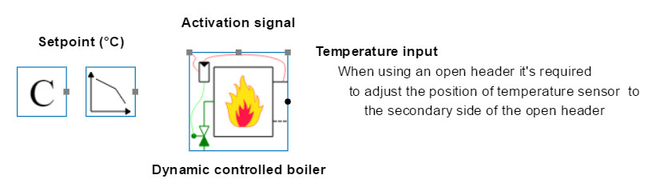
Dynamic controlled boiler
The dynamic boiler model is a more detailed boiler model than the "boiler with setpoint". The boiler also uses the three-dimensional matrix to generate a fuel consumption and secondary heat flow. However, this BC has its own control loop, which controls a gas valve in function of the measured supply temperature. Therefore there are more parameters necessary than the "boiler with setpoint".
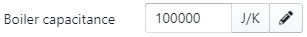
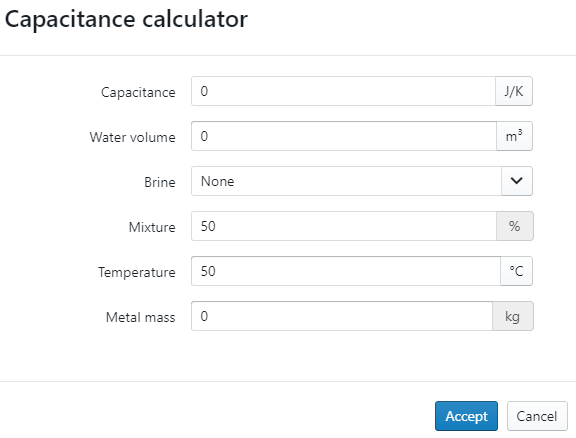
Besides the above-mentioned parameters, the user can also adjust the boiler capacitance (water content and mass of steel).
If the boiler capacitance isn't known but the water content and mass of steel is known, the user can click on the "pencil" icon and enter these aspects into the capacitance calculator.
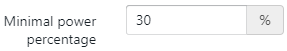
The minimal power percentage can be changed depending on the type of boiler.
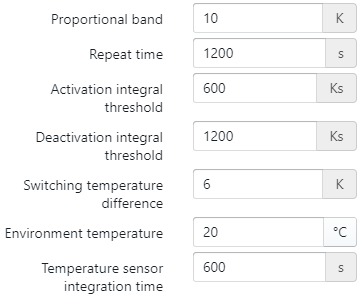
Boilers also typically have thermal losses to the environment, which can be included by entering a certain UA-value. This UA value (W/K) represents the thermal power (W) lost depending on the temperature difference (K) of the boiler and the environment. The environment temperature can also be changed by the user. In default, however, the thermal loss to the environment is indirectly included in the efficiency table, that's why the UA value is set to zero.
Furthermore, different control parameters are needed like the proportional band, repeat time, integral thresholds, etc. for accurate and stable control of the boiler. The default values and the control strategy are set resulting out of thorough communications with boiler manufacturers. If the user desires to change these, it's recommended to first contact one of our consultants.
Heat flow controlled boiler
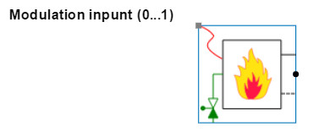
The heat flow controlled boiler is similar to the dynamic model with the only exception that this model has no internal control loop. The user has to apply a control loop on the boiler model, the input on this model is a power modulation signal (0...1). This model is primarily used for making a cascade control between several boilers or for educational purposes. The necessary parameters for this boiler model are mentioned above.
Electric boiler with setpoint
The electric boiler with setpoint is the same as the "boiler with setpoint" with the only exception that the default efficiency table is different in default. The efficiency of an electric boiler is typically 99%, so the efficiency table is just filled with one row resulting in a constant efficiency independent of the modulation, return temperature, and flow rate.
Examples of boiler concepts can be found in our Hysopt Inspiration Library with the following link Boiler.